Short History pyramids of Egypt
The pyramids of Egypt are some of the most recognizable and iconic structures in the world. They are a testament to the incredible engineering and architectural skills of the ancient Egyptians, as well as their deep religious beliefs and culture.
The first pyramids were built around 4,500 years ago during the Old Kingdom period of Ancient Egypt. Prior to this time, pharaohs were buried in mastabas, which were flat-roofed rectangular structures with sloping sides. The mastabas were made of mud bricks and were often decorated with scenes from the pharaoh’s life and offerings to the gods.
The first pyramid was built for Pharaoh Djoser by his architect, Imhotep. It was called the Step Pyramid and was located in Saqqara, near Memphis. The Step Pyramid was a series of mastabas stacked on top of each other to create a pyramid shape. The structure was around 60 meters high and was made of limestone. It was surrounded by a large complex that included courtyards, temples, and other buildings.

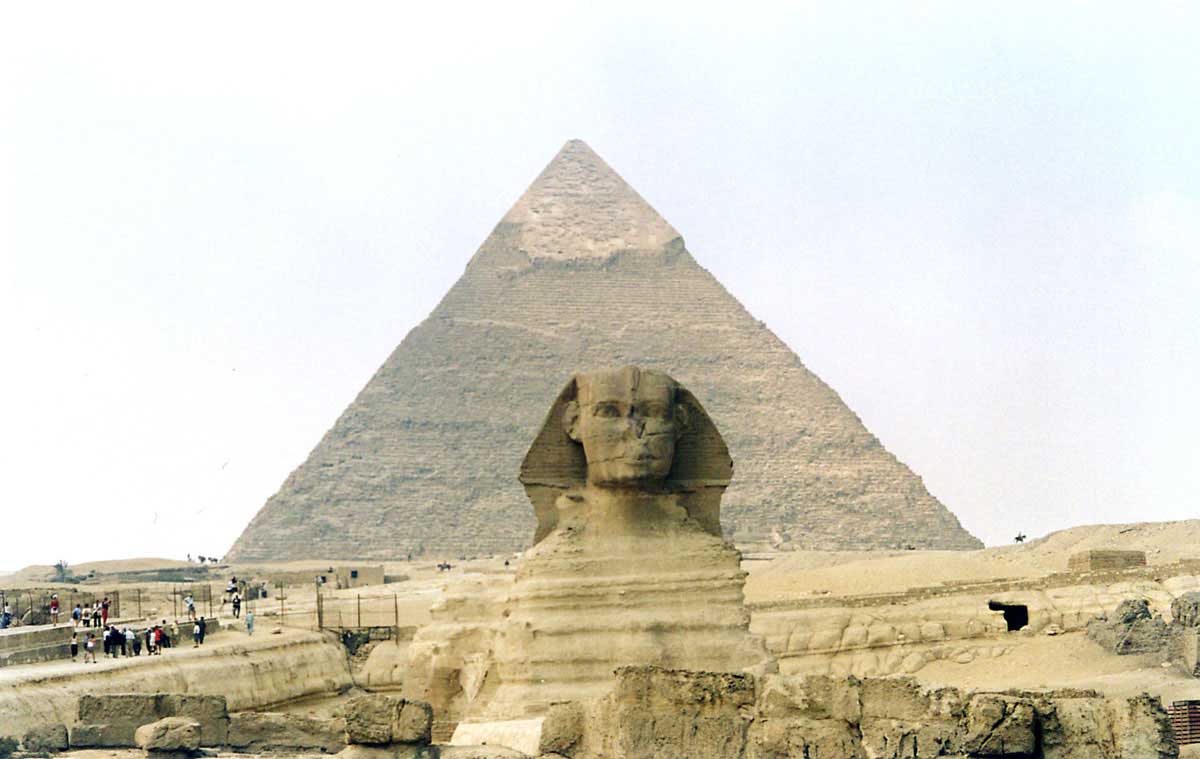
After the Step Pyramid, pharaohs began to build more traditional pyramids. The Great Pyramid of Giza is the most famous of these pyramids and is the largest pyramid ever built. It was built for Pharaoh Khufu and is located in Giza, near Cairo. The Great Pyramid is around 140 meters high and was built using around 2.3 million limestone blocks, each weighing around 2.5 tons.
The construction of the pyramids was a massive undertaking that required a huge amount of labor and resources. It is estimated that it took around 20 years to build the Great Pyramid and that around 100,000 workers were involved in the construction. These workers were not slaves, as is often believed, but were instead skilled craftsmen and farmers who were conscripted to work on the project.
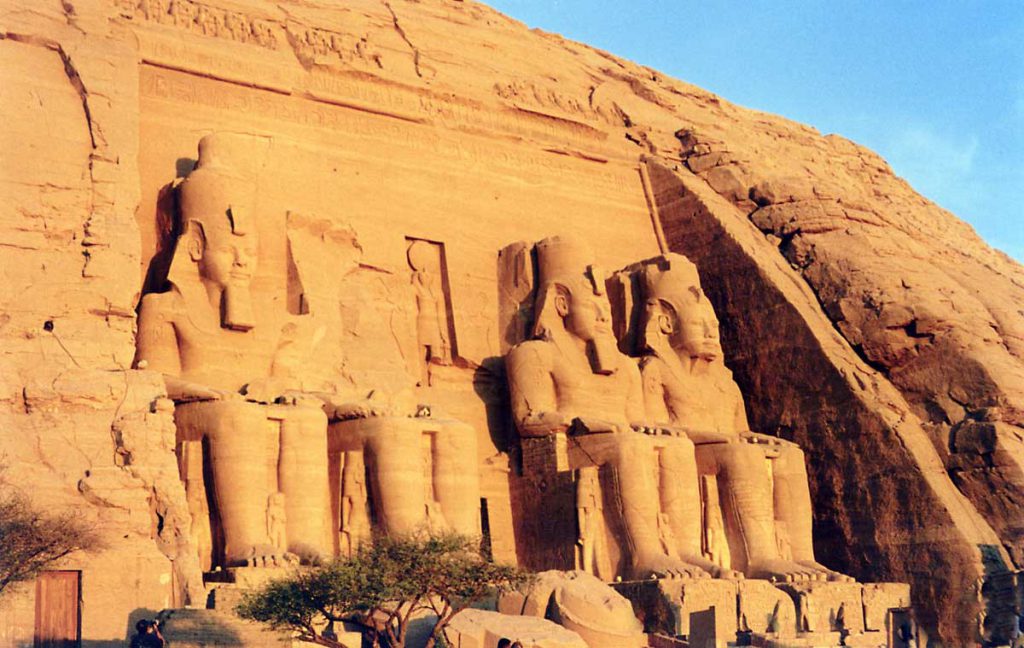
The pyramids were built to serve as tombs for the pharaohs and their consorts. It was believed that the pharaohs were divine beings who needed to be properly buried and equipped for the afterlife. The pharaoh’s body was mummified and placed in a sarcophagus inside the pyramid. The pyramid was then sealed with blocks of stone to prevent anyone from entering the tomb.
Inside the pyramids, there were often elaborate burial chambers and other rooms. These rooms were filled with offerings of food, jewelry, and other items that the pharaoh might need in the afterlife. The walls of the rooms were often decorated with scenes from the pharaoh’s life and hieroglyphic inscriptions that told the story of their journey to the afterlife.
The construction of the pyramids declined after the Old Kingdom period, and pharaohs began to be buried in smaller, less elaborate tombs. However, the pyramids continued to be an important part of Egyptian culture and religion. They were seen as symbols of the pharaoh’s power and their connection to the gods.
Today, the pyramids of Egypt continue to fascinate people from all over the world. They are a testament to the incredible engineering skills of the ancient Egyptians and serve as a reminder of the rich history and culture of this ancient civilization.